How Does a Keto Diet Work: Keto Hacks
The ketogenic (keto) diet has surged in popularity over recent years, celebrated for its potential weight loss and health benefits. But how does this low-carb, high-fat dietary regimen actually influence the body? The underlying mechanism centers around altering our primary energy source from carbohydrates to fats, pushing our bodies into a metabolic state called ketosis.
In this state, the body efficiently burns fat for energy and produces ketone bodies in the liver, which can also be used as a source of fuel, especially for the brain. In this introduction, we will delve into the science behind the keto diet, its benefits, potential side effects, and its overall impact on our body’s physiology. Whether you’re considering starting the diet or simply curious about its workings, understanding the biochemical changes it triggers can provide clarity on its widespread effects.
How Does a Keto Diet Work?
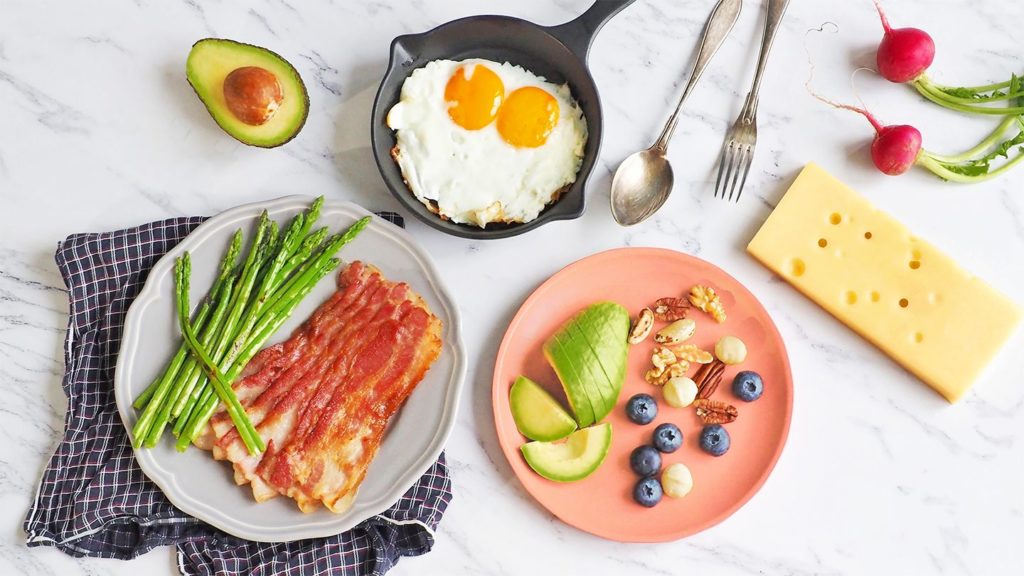

A keto diet, renowned for its low carbohydrate and high-fat regimen, instigates a series of metabolic shifts in the body, steering it to utilize fat as the primary source of energy. Here’s a step-by-step guide to understanding how a keto diet works:
Step 1: Carbohydrate Restriction
- Lowering Carbohydrate Intake: The initial step involves substantially reducing carbohydrate intake to about 5-10% of daily caloric intake. This is usually below 50 grams of net carbs per day.
- Eliminating Sugary Foods: Refined sugars and high-carb foods are eliminated from the diet to prevent spikes in blood sugar levels.
Step 2: Entering Ketosis
- Depletion of Glycogen Reserves: With reduced carb intake, the body starts depleting its glycogen stores, which are the primary storage form of glucose.
- Initiation of Ketosis: As glycogen stores wane, the body enters a metabolic state known as ketosis, wherein it begins to burn fat for energy.
Step 3: Fat Metabolism
- Increased Fat Intake: Parallelly, the diet necessitates a higher intake of fats (about 70-80% of total calories), fostering the body’s ability to metabolize fats more efficiently.
- Fat Conversion to Ketones: In the liver, the fats are broken down into fatty acids and glycerol. The fatty acids further undergo beta-oxidation to produce ketone bodies: acetoacetate, beta-hydroxybutyrate, and acetone.
Step 4: Utilizing Ketones for Energy
- Ketones as Fuel: These ketone bodies now act as an alternative energy source, supplying fuel to vital organs like the brain, which cannot utilize fatty acids directly for energy.
- Adaptation to Ketosis: As the body adapts to ketosis, it becomes more efficient in utilizing ketones for energy, sparing muscle mass from being broken down for glucose production.
Step 5: Physiological Adjustments
- Weight Loss: The keto diet often leads to weight loss due to reduced insulin levels and the body utilizing its fat stores.
- Appetite Regulation: Many individuals on a keto diet report decreased appetite and cravings, which is partly attributed to stabilized blood sugar levels and altered gut hormone signals.
Step 6: Maintenance and Adaptation
- Nutrient Micromanagement: To prevent nutrient deficiencies, attention is given to nutrient-dense foods and possibly supplementing with essential nutrients like vitamins and minerals.
- Metabolic Flexibility: Over time, the body develops metabolic flexibility, the ability to switch between carbohydrates and fats as energy sources based on dietary intake.
Step 7: Monitoring and Adjusting
- Monitoring Progress: Individuals on a keto diet are encouraged to monitor their progress and make necessary adjustments based on their health goals and responses.
- Consulting Healthcare Provider: Before and during the diet, consulting a healthcare provider to assess individual health conditions and adapt the diet accordingly is recommended.
Tips for successfully following a keto diet
Certainly! The ketogenic (keto) diet is a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet. When followed correctly, it can have various health benefits, including weight loss and improved metabolic health. Here are some tips for successfully adhering to a keto diet:
Educate Yourself:
Understand the science behind keto and how it works. The main goal of a ketogenic diet is to shift your body from burning carbohydrates for fuel to burning fat. This is achieved by significantly reducing carbohydrate intake and increasing fat intake.
Plan Your Meals and Snacks:
Having a meal plan will prevent making poor food choices when hungry. Plan your meals for the week, including snacks, and do your grocery shopping accordingly. Keep keto-friendly snacks handy, like nuts, cheese, and olives, to prevent reaching for carb-heavy alternatives.
Monitor Macros:
A keto diet is not just about reducing carbs but also about balancing fats and proteins. Using a food tracking app can be beneficial to ensure you’re meeting your macro goals (roughly 70-75% fat, 20-25% protein, and 5-10% carbs).
Stay Hydrated and Balance Electrolytes:
As your body adjusts to keto, you might lose more fluids and electrolytes, leading to the “keto flu”. Combat this by drinking plenty of water, and consider increasing your intake of salt and foods rich in potassium and magnesium, like avocados and leafy greens.
Listen to Your Body:
Everyone’s experience with keto can be different. Pay attention to how you feel, and adjust as necessary. For some, dairy or certain sweeteners can cause stalls in weight loss or other issues. Periodic self-checks and maybe even keeping a journal can help you pinpoint any foods or habits that don’t sit well with your body.
Don’t Obsess Over the Scale:
Weight loss is one of the most popular reasons people turn to the keto diet, but weight can fluctuate daily for a variety of reasons. Instead of focusing solely on the scale, take note of other benefits you might be experiencing, such as increased energy, clearer skin, or improved mental clarity. Also, consider taking measurements or noting how your clothes fit, as these can be better indicators of fat loss.
Final Thoughts
To sum up, the keto diet is a low-carb, high-fat eating plan that can aid in weight loss and enhance overall well-being. By decreasing carbohydrate consumption and increasing fat intake, the body enters a state of ketosis, where it utilizes fat as fuel instead of glucose. This metabolic transition can result in swift weight loss and heightened energy levels.
Moreover, research has demonstrated that the keto diet improves insulin sensitivity and reduces inflammation within the body. However, it is crucial to acknowledge that the keto diet may not be suitable for everyone and should be approached cautiously. It is always advisable to seek guidance from a healthcare professional before embarking on any new dietary or lifestyle changes. Take charge of your health and carefully consider if the keto diet aligns with your needs!
FAQs
What can I eat on a keto diet?
You can include foods like meats, fatty fish, eggs, dairy products (high in fat), nuts and seeds, healthy oils (olive oil, coconut oil), low-carb vegetables (leafy greens, broccoli), and some fruits in moderation.
Can I eat carbs occasionally while following a ketogenic lifestyle?
To maintain ketosis effectively, it’s best to limit carbohydrate intake consistently. However, some people may be able to consume small amounts of carbs occasionally without being completely kicked out of ketosis.